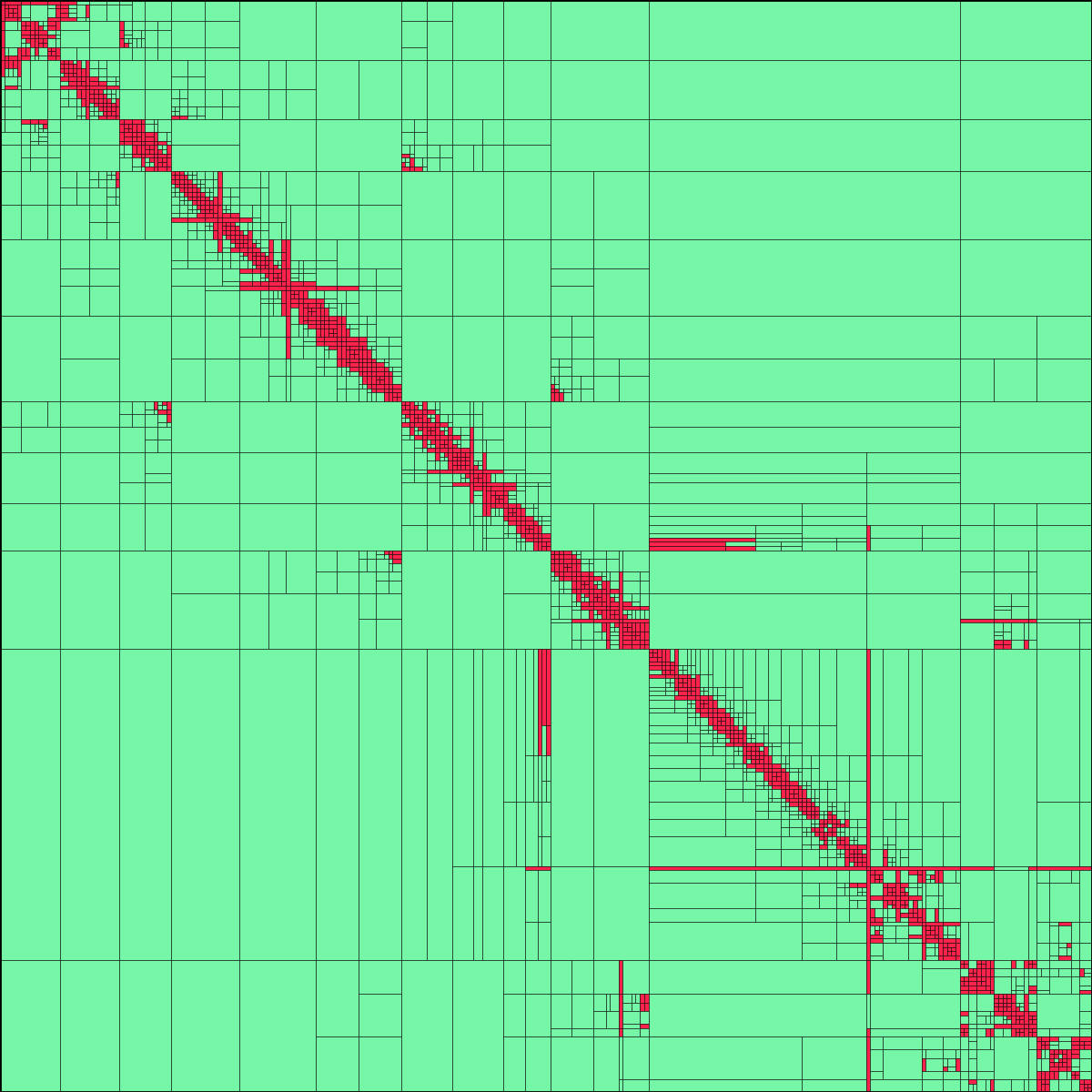
"""This is an implementation of the one-dimensional model example described in :cite:`thesis`.
It shows a typical use-case of hierarchical matrices:
.. admonition:: Integral Equation
.. math::
\int_0^1 \frac{1}{2\pi}\log |x-y| u(y) dy = g
for :math:`x \in [0,1]`.
After Galerkin discretization, we end up with a linear system
.. math::
\mathbf{A}^{\\text{Gal}} \cdot \\alpha = \mathbf{g}
where
.. math::
\mathbf{A}^{\\text{Gal}}_{t,\\tau}:= \int_{t}\int_{\\tau} \log |x-y| dy dx
To determine admissible blocks we start by building the geometric objects:
.. code-block:: python
midpoints = [((i + 0.5)/n,) for i in xrange(n)]
intervals = {p: (p[0] - 0.5/n, p[0] + 0.5/n) for p in midpoints}
grid = HierMat.Grid(points=midpoints, supports=intervals)
cluster = HierMat.Cluster(grid=grid)
unit_cuboid = HierMat.Cuboid([0], [1])
strategy = HierMat.RegularCuboid(cluster=cluster, cuboid=unit_cuboid)
cluster_tree = HierMat.build_cluster_tree(splitable=strategy, max_leaf_size=n_min)
block_cluster_tree = HierMat.build_block_cluster_tree(left_cluster_tree=cluster_tree,
right_cluster_tree=cluster_tree,
admissible_function=HierMat.admissible
)
With the structure established, we can produce the hierarchical matrix:
.. code-block:: python
hmat = HierMat.build_hmatrix(block_cluster_tree=block_cluster_tree,
generate_rmat_function=lambda bct: galerkin_1d_rank_k(bct, max_rank),
generate_full_matrix_function=galerkin_1d_full
)
"""
import numpy
import scipy.integrate as integrate
import HierMat
import os
import math
[docs]def model_1d(n=2 ** 3, max_rank=2, n_min=2):
"""This is an implementation of the one-dimensional model example described in :cite:`thesis`.
:param n: number of discretization points
:type n: int
:param max_rank: max rank of the low-rank approximation
:type max_rank: int
:param n_min: minimal leaf size for cluster trees
:type n_min: int
:return: error
"""
midpoints = [((i + 0.5)/n,) for i in xrange(n)]
intervals = {p: (p[0] - 0.5/n, p[0] + 0.5/n) for p in midpoints}
grid = HierMat.Grid(points=midpoints, supports=intervals)
cluster = HierMat.Cluster(grid=grid)
unit_cuboid = HierMat.Cuboid([0], [1])
strategy = HierMat.RegularCuboid(cluster=cluster, cuboid=unit_cuboid)
cluster_tree = HierMat.build_cluster_tree(splitable=strategy, max_leaf_size=n_min)
HierMat.export(cluster_tree, form='dot', out_file='galerkin_1d_ct.dot')
os.system('dot -Tpng galerkin_1d_ct.dot > model_1d-ct.png')
os.system('dot -Tsvg galerkin_1d_ct.dot > model_1d-ct.svg')
block_cluster_tree = HierMat.build_block_cluster_tree(left_cluster_tree=cluster_tree,
right_cluster_tree=cluster_tree,
admissible_function=HierMat.admissible
)
HierMat.plot(block_cluster_tree, filename='model_1d-bct.png')
hmat = HierMat.build_hmatrix(block_cluster_tree=block_cluster_tree,
generate_rmat_function=lambda bct: galerkin_1d_rank_k(bct, max_rank),
generate_full_matrix_function=galerkin_1d_full
)
hmat_full = hmat.to_matrix()
galerkin_full = galerkin_1d_full(block_cluster_tree)
HierMat.export(hmat, form='bin', out_file='hmat.bin')
numpy.savetxt('hmat_full.txt', hmat_full)
numpy.savetxt('gallmat_full.txt', galerkin_full)
res = numpy.linalg.norm(hmat_full - galerkin_full)
return res
[docs]def kerlog(x):
"""kerlog function as in :cite:`thesis`.
.. math::
kerlog(x):= x^2 \left( \log(\Vert x \Vert) - \\frac{1}{2} \\right)
:param x: real number
:type x: float
:return: :math:`x^2 ( \log(\Vert x \Vert) - \\frac{1}{2} )`
:rtype: float
"""
out = x**2 * (numpy.log(abs(x))-0.5)
if math.isnan(out):
return 0
else:
return out
[docs]def ker(x, y):
"""Kernel to integrate
.. math::
ker(x, y):= \log\left(\Vert x - y \Vert\\right)
:param x: real number
:type x: float
:param y: real number
:type y: float
:return: :math:`\log\left(\Vert x - y \Vert\\right)`
:rtype: float
"""
return numpy.log(abs(x - y)) / (2 * numpy.pi)
[docs]def galerkin_1d_rank_k(block_cluster_tree, max_rank):
"""Low-rank approximation of the kernel
.. math::
R: &= A \cdot B^T
A_{\\tau, k}: &= \int_\\tau \log \Vert x-y_k\Vert dx
B_{\\tau, k}: &= \int_\\tau \mathcal{L}_k(y) dy
:param block_cluster_tree: admissible block cluster tree
:type block_cluster_tree: HierMat.BlockClusterTree
:param max_rank: separation rank
:type max_rank: int
:return:
"""
# initialize output
x_length, y_length = block_cluster_tree.shape()
left_matrix = numpy.matrix(numpy.zeros((x_length, max_rank)))
right_matrix = numpy.matrix(numpy.zeros((y_length, max_rank)))
# determine the y-interval
y_low = block_cluster_tree.right_clustertree.get_grid_item_support_by_index(0)[0]
y_high = block_cluster_tree.right_clustertree.get_grid_item_support_by_index(-1)[1]
# build Chebyshev nodes
y_nodes = get_chebyshev_interpol_points(max_rank, y_low, y_high)
# build left_hand matrix
for y_count, y_k in enumerate(y_nodes):
for i in xrange(x_length):
lower, upper = block_cluster_tree.left_clustertree.get_grid_item_support_by_index(i)
left_matrix[i, y_count] = integrate.quad(lambda x: ker(x, y_k), lower, upper)[0]
for j in xrange(y_length):
lower, upper = block_cluster_tree.right_clustertree.get_grid_item_support_by_index(j)
def lagrange(y):
res = 1.0
for y_i in y_nodes:
if y_i != y_k:
res *= (y - y_i) / (y_k - y_i)
return res
right_matrix[j, y_count] = integrate.quad(lagrange, lower, upper)[0]
return HierMat.RMat(left_mat=left_matrix, right_mat=right_matrix, max_rank=max_rank)
[docs]def galerkin_1d_full(block_cluster_tree):
"""Exact calculation of the integral
.. math::
A_{i,j}=A_{\\tau,t}^{Gal}=\int_t\int_\\tau\log\Vert x-y\Vert \;dydx
:param block_cluster_tree: inadmissible block cluster tree
:type block_cluster_tree: HierMat.BlockClusterTree
:return: matrix with same shape as block_cluster_tree.shape()
:rtype: numpy.matrix
"""
x_length, y_length = block_cluster_tree.shape()
out_matrix = numpy.matrix(numpy.zeros((x_length, y_length)))
for i in xrange(x_length):
for j in xrange(y_length):
c, d = block_cluster_tree.left_clustertree.get_grid_item_support_by_index(i)
a, b = block_cluster_tree.right_clustertree.get_grid_item_support_by_index(j)
out_matrix[i, j] = (-kerlog(d - b) + kerlog(c - b) + kerlog(d - a) - kerlog(c - a)) / (4 * numpy.pi) \
+ (a - b) * (d - c) / (2 * numpy.pi)
return out_matrix
[docs]def get_chebyshev_interpol_points(points, lower=0, upper=1):
"""Get Chebyshev interpolation points on interval :math:`(a, b)`.
.. math::
\\frac{1}{2} (a + b) + \\frac{1}{2} (b - a) \cos\left(\\frac{2k+1}{2n}\pi\\right)
for :math:`k=0, ..., \\text{points} - 1`
:param points: number of points
:type points: int
:param lower: :math:`a`, (default 0)
:type lower: float
:param upper: :math:`b`, (default 0)
:type upper: float
:return: :math:`\\frac{1}{2} (a + b) + \\frac{1}{2} (b - a) \cos\left(\\frac{2k+1}{2n}\pi\\right)`
:rtype: list(floats)
"""
return [(lower + upper + (upper - lower) * numpy.cos((2 * k + 1) * numpy.pi / (2 * points))) / 2
for k in xrange(points)]
if __name__ == '__main__':
model_1d(n=2**8, max_rank=5, n_min=8)